Musculoskeletal Disorders
Back & Neck
Foot & Ancle
Hand & Wrist
Hip & Pelvis
Knee & Lower Leg
Athletic injuries
Rotator Cuff Tear
A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of shoulder pain and disability among adults. A torn rotator cuff may weaken your shoulder.
A rotator cuff tear is a common cause of shoulder pain and disability among adults. A torn rotator cuff may weaken your shoulder.
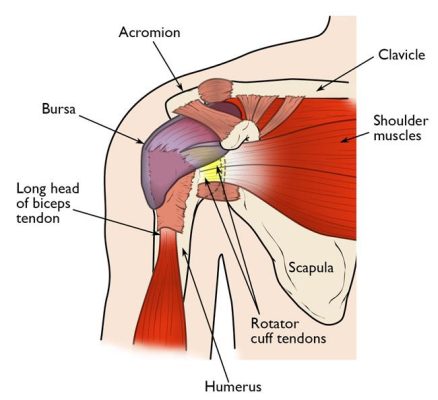
The rotator cuff tendons cover the head of the humerus (upper arm bone), helping you to raise and rotate your arm.
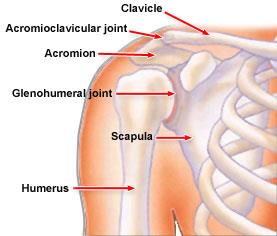
The shoulder is made up of 3 bones: humerus, scapula, and the clavicle.
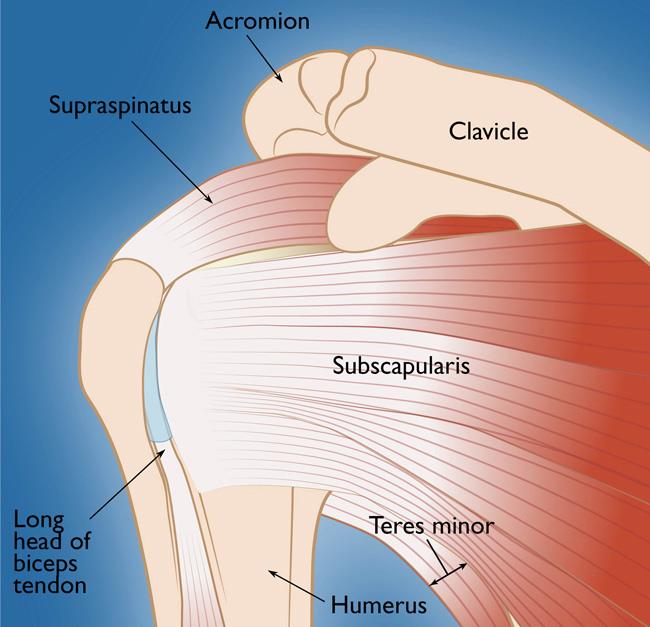
Your arm is kept in the shoulder socket by the rotator cuff. These muscles and tendons form a covering around the head of the upper arm bone and attach it to the shoulder blade.Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon.
There are different types of tears.
- Partial tear-not completely detach the tendon from the bone. It is called partial because the tear goes only partially through the thickness of the tendon. The tendon is still attached to the bone, but it is thinned.
- Full-thickness tear- there is detachment of part of the tendon from the bone.
There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears: injury and wear (degeneration).
The goal of any treatment is to reduce pain and restore function. There are several treatment options for a rotator cuff tear, and the best option is different for every person.That depends on:
- age
- activity level
- general health
- The type of tear
Nonsurgical Treatment
In 80 to 85% , nonsurgical treatment relieves pain and improves function in the shoulder.
Nonsurgical treatment options may include:
- Rest.
- Avoid any activities that cause shoulder pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Strengthening exercises and physical therapy..
- Steroid injection.
The shoulder is made up of 3 bones: humerus, scapula, and the clavicle.
Your arm is kept in the shoulder socket by the rotator cuff. These muscles and tendons form a covering around the head of the upper arm bone and attach it to the shoulder blade.Most tears occur in the supraspinatus tendon.
There are different types of tears.
- Partial tear-not completely detach the tendon from the bone. It is called partial because the tear goes only partially through the thickness of the tendon. The tendon is still attached to the bone, but it is thinned.
- Full-thickness tear- there is detachment of part of the tendon from the bone.
There are two main causes of rotator cuff tears: injury and wear (degeneration).
The goal of any treatment is to reduce pain and restore function. There are several treatment options for a rotator cuff tear, and the best option is different for every person.That depends on:
- age
- activity level
- general health
- The type of tear
Nonsurgical Treatment
In 80 to 85% , nonsurgical treatment relieves pain and improves function in the shoulder.
Nonsurgical treatment options may include:
- Rest.
- Avoid any activities that cause shoulder pain.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Strengthening exercises and physical therapy..
- Steroid injection.
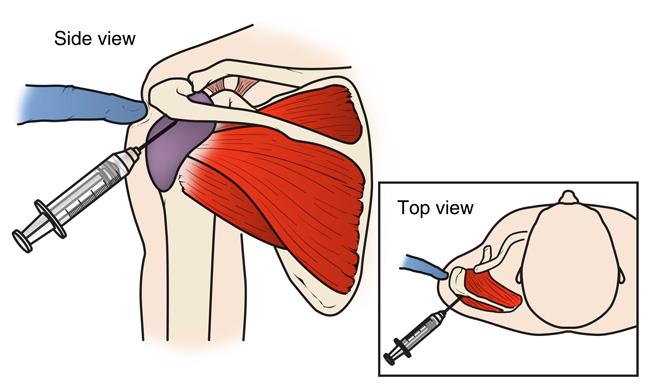
A cortisone injection may relieve painful symptoms.
if your pain does not improve with nonsurgical methods. Continued pain is the main indication for surgery. Surgery to repair a torn rotator cuff most often involves re-attaching the tendon to the head of humerus.


 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά